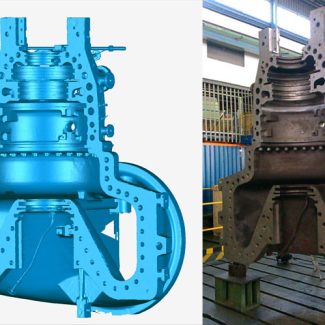
Product development is a fast-paced industry that requires high-quality prototypes. This is because we can comfortably test and improve designs according to our requirements at the early stages. This procedure has been transformed by 3D printing.
Certainly, it offers an adaptable and efficient way to turn digital models directly into tangible designs.
We’ll look at how to use 3D printing to make high-quality prototypes in this article.
Detailed Design for High-Quality Prototype
Start by creating a 3D model of the prototype that is properly detailed. You should make sure that the design you are creating is accurate and precise by using reliable tools like CAD software.
Moreover, you should pay attention to intricate details and consider the material properties accordingly.
Selection of Material for High-Quality Prototype
You should select the appropriate 3D printing material considering the prototype’s need. Typical materials include resin for complex, highly detailed models, ABS for long-term reliability, and PLA for quick prototyping.
Furthermore, you should make sure that your selected material has the desired effects on the finished product.
Printer Calibration for High-Quality Prototype
Proper calibration of 3D printers is essential to ensure peak performance. This includes making necessary adjustments to the temperature, bed leveling, and nozzle height.
Hence, achieving the required level of accuracy and thoroughness requires proper calibration.
Layer Height and Resolution
Also, don’t forget to fine-tune our printer settings for layer height and resolution. Lower layer heights result in smoother surfaces but may increase print time.
Therefore, you should balance these factors to achieve the desired level of accuracy and precision while maintaining efficiency.
Crucial Role of Support Structures in 3D Printing
Support structures in high-quality 3D printing play a vital role in ensuring the success of intricate and overhanging designs. These elements act as scaffolding during the printing process.
In addition, they prevent deformations and ensure the structural integrity of the final product.
Post-Processing Techniques
You must refine the prototype after printing. Sanding, smoothing, and painting can enhance the final appearance. Additionally, you should consider post-curing for resin prints to improve strengths and surface finish.
Testing and Iteration
Now, it’s time to conduct both functional and visual tests on the printed prototype. In this way, you can determine what needs to be improved to make the necessary design iterations.
Scaling for Production
When the prototype adheres to requirements, you should adapt the design for mass manufacturing. Always choose materials that would work well for the finished product.
Documentation of High-Quality 3D Printing
Always maintain detailed documentation of the entire 3D printing process. This includes design iterations, material choices, printer settings, and any challenges faced.
This comprehensive documentation ensures consistency and reliability. It also facilitates future changes or upgrades.
Careful material selection, calibration, and post-processing are essential while using 3D printing to develop accurate prototypes. In addition, prototyping effectiveness is also enhanced by prioritizing testing and iterations.
To summarise, the ability to produce high-quality prototypes requires a combination of technology, skill, and a dedication to ongoing innovation.